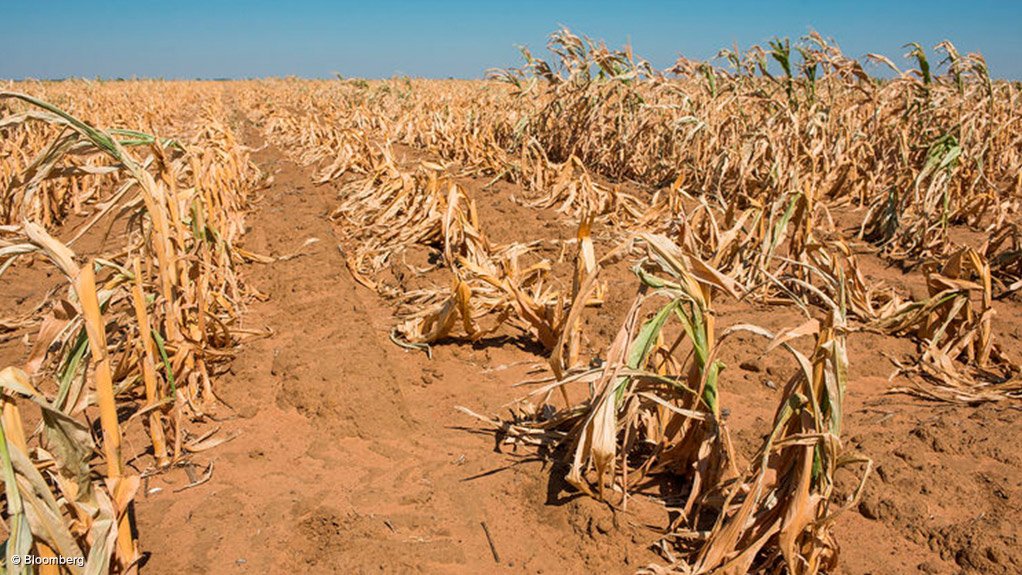
El Niño scorches Southern Africa with driest February on record
A swathe of Southern Africa suffered the driest February in decades that wiped out crops, precipitated power shortages and threatened to send already high food prices surging further.
Last month, large parts of Zambia, Botswana and Zimbabwe had the least rainfall — or close to it — since records began in 1981, early data from the University of California Santa Barbara’s Climate Hazards Center show. The center based its preliminary appraisal mainly on satellite-based rainfall estimates, with a final assessment due next week that will include more rainfall gauge observations.
The dry spell, blamed on the El Niño weather phenomenon, is the latest indicator of how severely Africa is being impacted by extreme weather events that scientists say are becoming increasingly frequent and severe because of climate change — even though it produces far less global-warming gases than developed regions.
Zambian President Hakainde Hichilema last week declared the drought a national disaster — an estimated 45% of planted areas have been destroyed just as the staple corn crop should be maturing. In Zimbabwe, some farmers have given up trying to grow and harvest their crops, allowing cattle to graze on what’s left. Water flows in the Zambezi River, which powers turbines that both nations rely on for electricity, are less than a quarter of what they were a year ago.
“This drought has devastating consequences,” Hichilema said in a national address. “The destruction caused by the prolonged drought spell is immense.”
The cost of corn in Zambia surged an average 76% in February from a year ago. In neighbouring Zimbabwe, US dollar prices for the cereal have shown a similar increase since December alone, according to the Famine Early Warning Systems Network. In some areas, prices doubled within three months.
Zimbabwe’s government has warned that the 2024 harvest may be half of last year’s. The local grain millers association plans to import as much as 1.1-million tons of corn from neighboring South Africa and South America over the next year, the state-owned Herald newspaper reported Feb. 28. The World Food Programme anticipates that about a quarter of the rural population will run short of grain in the first quarter.“Food supply constraints brought on by dry conditions will place upward pressure on inflation in the region in 2024,” said Yvonne Mhango, Africa Economist at Bloomberg Economics. “This will likely mean high rates for longer.”
Large parts of Botswana have also been scorched by El Niño, with the Botswana Meteorological Services noting that the vast majority of the country was receiving significantly less rain than normal. Farmers who receive government support planted less than half the area in the current season than they did in the previous one.
In Namibia, water levels in dams are already at dangerously low levels. The main reservoir supplying the capital, Windhoek, is only 11% full and dropping, according to Andries Kok, a spokesperson for the national water utility.
The drought is set to dampen output beyond agriculture. Zambia relies on hydropower for about 85% of its electricity generation and water levels at Kariba, the world’s biggest man-made freshwater lake which is fed by the Zambezi, have plunged to 15% of storage capacity — meaning power will have to be rationed. Zimbabwe has already increase the severity of it’s rolling blackouts.
Kariba's inflows are so meagre this season they could end up among the lowest on record, according to the government agency that regulates the reservoir.
El Niño is mainly a seasonal phenomenon that makes extreme weather and climate events more likely, according to the World Meteorological Organization. The current event is one of the five strongest ever recorded, and has contributed to drier and warmer conditions in parts of southern Africa, it said in a March 5 statement. Temperatures were 4 °C to 5 °C higher than the February average, it said.
Comments
Press Office
Announcements
What's On
Subscribe to improve your user experience...
Option 1 (equivalent of R125 a month):
Receive a weekly copy of Creamer Media's Engineering News & Mining Weekly magazine
(print copy for those in South Africa and e-magazine for those outside of South Africa)
Receive daily email newsletters
Access to full search results
Access archive of magazine back copies
Access to Projects in Progress
Access to ONE Research Report of your choice in PDF format
Option 2 (equivalent of R375 a month):
All benefits from Option 1
PLUS
Access to Creamer Media's Research Channel Africa for ALL Research Reports, in PDF format, on various industrial and mining sectors
including Electricity; Water; Energy Transition; Hydrogen; Roads, Rail and Ports; Coal; Gold; Platinum; Battery Metals; etc.
Already a subscriber?
Forgotten your password?
Receive weekly copy of Creamer Media's Engineering News & Mining Weekly magazine (print copy for those in South Africa and e-magazine for those outside of South Africa)
➕
Recieve daily email newsletters
➕
Access to full search results
➕
Access archive of magazine back copies
➕
Access to Projects in Progress
➕
Access to ONE Research Report of your choice in PDF format
RESEARCH CHANNEL AFRICA
R4500 (equivalent of R375 a month)
SUBSCRIBEAll benefits from Option 1
➕
Access to Creamer Media's Research Channel Africa for ALL Research Reports on various industrial and mining sectors, in PDF format, including on:
Electricity
➕
Water
➕
Energy Transition
➕
Hydrogen
➕
Roads, Rail and Ports
➕
Coal
➕
Gold
➕
Platinum
➕
Battery Metals
➕
etc.
Receive all benefits from Option 1 or Option 2 delivered to numerous people at your company
➕
Multiple User names and Passwords for simultaneous log-ins
➕
Intranet integration access to all in your organisation